India has a developing natural gas pipeline network, with a mix of operational and under-construction pipelines. As of December 2024, India had 25,124 km of operational natural gas pipelines, with an additional 10,676 km under construction or planned. The government aims to expand this network to create a National Gas Grid, enhancing natural gas accessibility across the country.
Liquefied natural gas, or LNG, must be super-cooled and stored in its liquid form at -260°F before being converted back into a gas. LNG must be in its gaseous form before it enters the domestic pipeline distribution system and is ultimately delivered to the end user. LNG can be used in vehicles, although CNG vehicles are more common.
While most natural gas fueling stations in India dispense CNG, a limited number of LNG fueling stations are available. Many LNG users are fleets that have private fueling infrastructure for their vehicles; however, numerous public LNG fueling sites are available to fleets. Large-scale liquefaction facilities provide LNG fuel for transportation nationwide, and LNG must be delivered to stations via trucks.
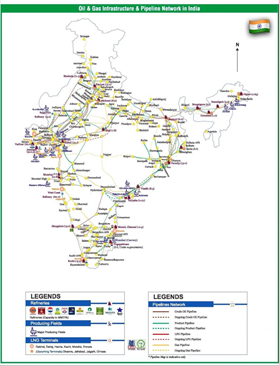
Oil & Gas Infrastructure and Pipeline Network in India as of 2025
In addition to distribution via the nation’s extensive pipeline network, renewable natural gas (RNG) can be dispensed at production sites, such as landfills or wastewater treatment plants with the ability to clean and upgrade biogas (the gaseous product of the decomposition of organic matter). Like conventional natural gas, RNG can be compressed or liquefied for use in vehicles.
Compressed Natural Gas Distribution
India’s Oil & Gas (O&G) sector is a cornerstone of its economic development, significantly contributing to its emergence as the world’s 4th largest economy. With strategic investments and robust infrastructure, the sector is poised to propel India to the 3rd position in the global economic hierarchy.
Natural Gas: Production & Sectoral Utilization
- Production: Increased from 92.2 MMSCMD in 2015 to 98.9 MMSCMD in 2025.
- Consumption: Rose from 140.4 MMSCMD in 2015 to 197.1 MMSCMD in 2025.
- YoY Sales Growth: Approximately 6.5%.
- Sector-wise Sales Distribution:
- Fertilizer: 29%
- City Gas Distribution (CGD): 21%
- Power: 12%
- Refinery: 8%
- Petrochemicals: 5%
City Gas Distribution (CGD) Network Expansion
- CNG Stations: Expanded to 8,067 stations.
- Domestic PNG Connections: 1.5 crore connections established.
- Commercial PNG: 45,373 connections.
- Industrial PNG: 20,461 connections.
- YoY Sales Growth: Approximately 15.2%
- Sales Profile:
- CNG: 60%
- Industrial PNG: 30%
- Domestic PNG: 8%
- Commercial PNG: 2%
Oil & Gas Infrastructure Network
- LNG Terminals: 8 terminals with a combined capacity of ~53 MMTPA.
- Depots & Terminals: 314 facilities.
- Aviation Fuel Stations (AFS): 302 stations.
- Pipeline Network:
- Crude Oil Pipelines: 10,445 km
- Product Pipelines: 24,130 km
- Natural Gas Pipelines: 33,151 km (23,752 km operational + 9,399 km under construction)
- Retail Outlets (ROs): 96,724 outlets, including 27,748 in rural areas.
- Average Sales per RO: 143.9 KL (MS & HSD)
Strategic Importance of Pipelines
The extensive network of underground pipelines for oil, gas, and CGD serves as the nation’s energy highways, offering the most economical, secure, and efficient mode of transportation for petroleum products.

Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.