As of 2025, more than 8,067 public compressed natural gas (CNG) fueling stations are available in India.
India is actively developing LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) infrastructure, including fueling stations, to support the adoption of LNG as a transportation fuel, particularly for heavy vehicles. Several companies are involved in this effort, with plans to establish a network of LNG stations along major highways and the Golden Quadrilateral.
1. LNG Terminals and Sourcing
- India has several operational LNG terminals, including those at Dahej and Kochi (operated by Petronet LNG Ltd.).
- Indian Oil also imports LNG and has a 5 MMTPA terminal on the east coast.
- Petronet LNG Ltd. is also developing a terminal in Andhra Pradesh.
2. LNG Fueling Stations:
- Companies like Indian Oil, Bharat Petroleum, and Hindustan Petroleum are setting up LNG stations.
- Indian Oil is planning to establish 20 LNG stations, while Bharat Petroleum and Hindustan Petroleum will each set up 11.
- GAIL (India) Limited is also involved in developing LNG stations along national highways.
- These stations are primarily aimed at heavy vehicles and buses.
- Chart Industries offers solutions for LNG fueling stations, including modular designs and integration with CNG.
3. Environmental and Economic Benefits
- LNG-powered trucks offer significant reductions in emissions compared to diesel trucks, including lower carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
- LNG trucks also produce less noise.
- LNG can be a competitively priced alternative to diesel, potentially leading to cost savings and emissions reductions.
- The adoption of LNG as a fuel for heavy vehicles is expected to contribute to a larger share of natural gas in India’s energy mix.
4. The Goal
- The development of LNG infrastructure aligns with India’s goal of reducing emissions and promoting cleaner transportation.
- The expansion of the LNG fueling network is expected to play a crucial role in achieving these goals.
Station Locations
Find natural gas (CNG and LNG) fueling stations by location or along a route. Use the Advanced Filters to search for private and planned stations, as well as natural gas fueling stations to match certain search criteria.
Infrastructure Development
CNG and LNG stations vary considerably. CNG stations require more equipment and configuration, while LNG stations require less equipment, but more safety precautions during fueling.
The Alternative Fueling Station Locator allows users to search for public and private CNG and LNG fueling stations. Suggest new natural gas stations for inclusion in the Station Locator using the Submit New Station form.
CNG Stations
There are essentially three types of CNG stations: fast-fill, time-fill, and a combination of these two. The type of station needed is dependent on the application. Typically, retail stations use fast-fill, and fleets that have central refueling and the ability to fill overnight use time-fill. All public fueling stations offer a fast-fill option.
LNG Stations
LNG stations are structurally similar to gasoline and diesel stations in that they have a storage tank, meters, and dispenser. LNG dispensers deliver fuel to vehicles at pressures of 30 to 120 psi. Because LNG is stored and dispensed as a super-cooled liquefied gas, protective clothing, face shield, and gloves are required when fueling a vehicle, and personnel must also be trained on fueling procedures.
There are three options for LNG fueling: mobile, containerized, and permanent large stations. In mobile fueling, LNG is delivered by a tanker truck that has on-board metering and dispensing equipment. A starter station, or containerized station, includes a storage tank, dispensing equipment, metering, and required containment. A permanent station has greater storage capacity and is tailored to meet fleets’ needs.
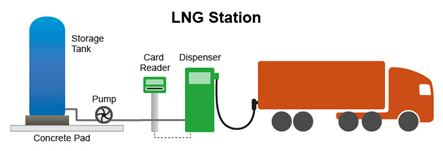
Example of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) station configuration.
Cost of Installation
The cost of installing natural gas infrastructure is influenced by station size, capacity, the type of natural gas (LNG, CNG, or both) dispensed, and the way natural gas is dispensed (fast-fill or time-fill). According to a report published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, costs of a CNG fueling station can range up to $1.8 million, depending on the size and application. Smaller fueling units average $10,000, including engineering, equipment, and installation. LNG fueling station costs are highly variable, ranging from one to several million dollars. Costs are dependent on factors such as storage capacity, station design, and the services needed to build it.
In addition, it is important to work with your local utility, which can help determine whether the appropriate level of gas pressure is available at your location, whether the gas quality and moisture content are appropriate, and whether your gas service can support the needed gas flow. Additional investment may be necessary to address these needs.
Safety
There are many safety guidelines that need to be considered when developing infrastructure, including the National Fire Prevention Association’s NFPA 52 Vehicular Natural Gas Fuel Systems Code, which applies to the design and installation requirements of CNG refueling facilities. Consult your local fire marshal or Clean Cities and Communities coalition for help.
